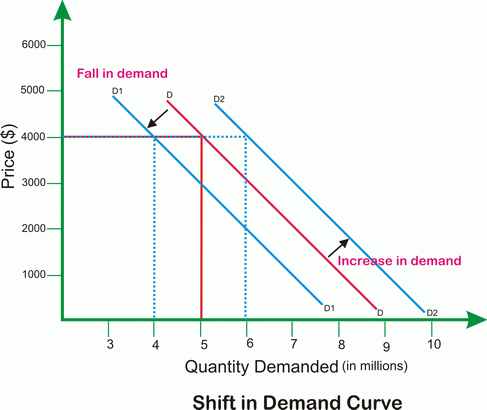
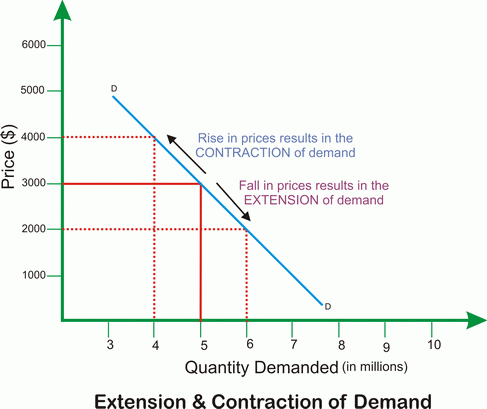
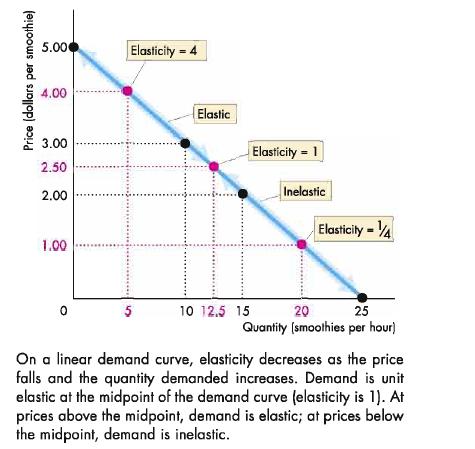
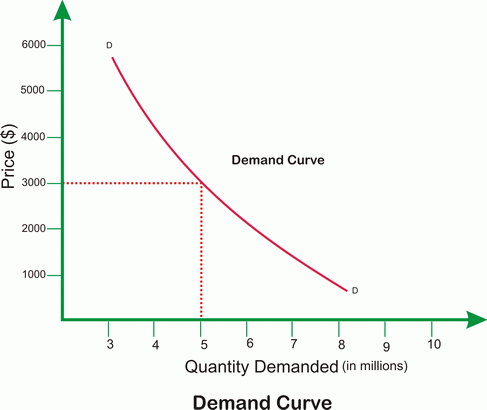
Definitions
Social Science and Economics
Social Science is defined as a branch of science that studies the
society and human behavior in it, including anthropology, communication
studies, criminology, economics, geography, history, political science,
psychology, social studies, and sociology.
Economics is the branch of social science that deals with the
production and distribution and consumption of goods and services and
their management.
It is the study of how scarce resources are allocated to fulfil unlimited wants.
Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Economics is usually divided into two main branches:
Microeconomics, which examines the economic
behaviour of individual actors such as businesses, households, and
individuals, with a view to understand decision making in the face of
scarcity and the allocation consequences of these decisions.
Macroeconomics, which examines an economy as a whole
with a view to understanding the interaction between economic
aggregates such as national income, employment and inflation.
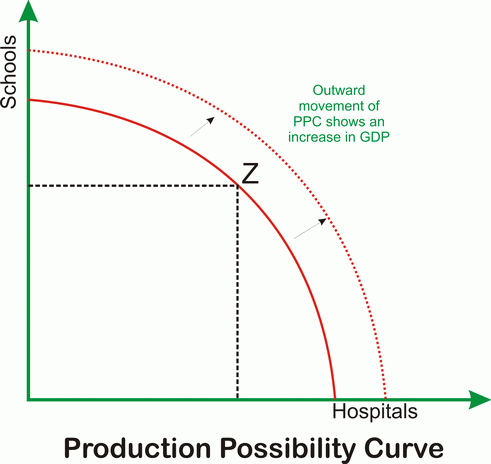
Economic growth is the increase of per capita gross
domestic product (GDP) or other measure of aggregate income. It is often
measured as the rate of change in GDP. Economic growth refers only to
the quantity of goods and services produced.
Economic development typically involves improvements
in a variety of indicators such as literacy rates, life expectancy, and
poverty rates. It is a measure of welfare in the economy. Human
Development Index (HDI) is one of the most commonly used development
measure.
Sustainable development is a pattern of resource use
that aims to meet human needs while preserving the environment so that
these needs can be met not only in the present, but also for future
generations. Economic development that meets the needs of the present
without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own
needs.
Free goods and Economics goods
Free goods are what is needed by the society and is
available without limits. The free good is a term used in economics to
describe a good that is not scarce. A free good is available in as great
a quantity as desired with zero opportunity cost to society.
Economics goods are consumable item that is useful
to people but scarce in relation to its demand, so that human effort is
required to obtain it.